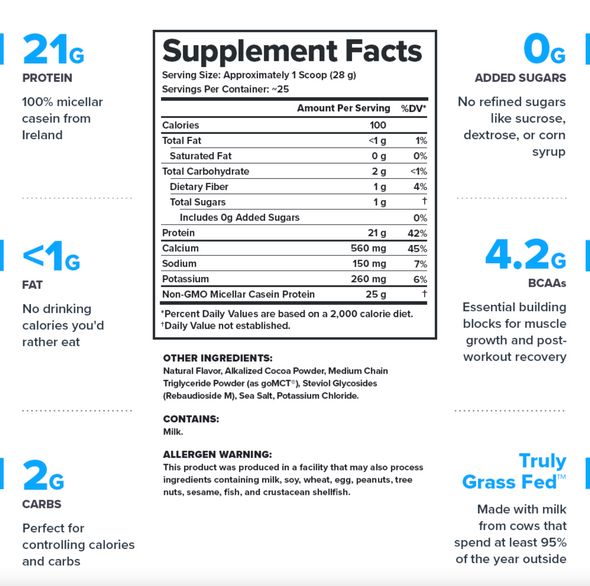
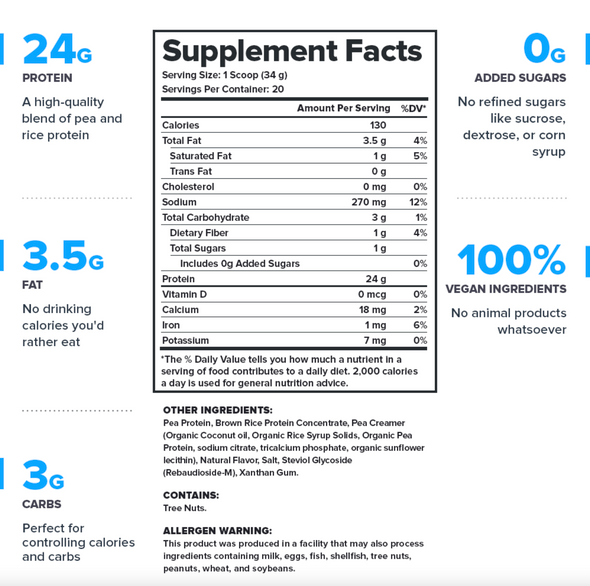
Creatine is a compound made up of the amino acids L-arginine, glycine, and methionine. Our body can produce creatine naturally, but it can also absorb and store creatine found in various foods like meat, eggs, and fish.
Creatine monohydrate is creatine with one molecule of water attached to it. This form of creatine has been around (and studied) for decades and is a tried-and-true winner, whereas other forms have failed to produce better results.
The creatine monohydrate in Recharge has also been micronized, which is a process that produces very fine particles that are more water soluble and easier to digest. Thus, micronized creatine monohydrate mixes better with liquid than the non-micronized form and is less likely to upset sensitive stomachs.
Research shows that supplementation with creatine monohydrate . . .
- Boosts muscle and strength gain
- Improves anaerobic endurance
- Reduces muscle damage and soreness from exercise
- Increases the amount of glycogen your muscles can store
- Helps preserve lean mass and strength while restricting calories
And in case you’re worried that creatine is bad for your kidneys, these claims have been horribly overblown. Creatine supplementation isn’t advised in cases of kidney disease treated by diuretics, but in healthy people, both short- and long-term usage of creatine has no harmful side effects.
The clinically effective dose of creatine monohydrate is 3 to 5 grams.